Shape Reconstruction
In the Reverse Engineering field an exhisting physical object is acquired through a 3D scanner, that produce as output a set of 3D coordinates on the surface of the object, and reconstructed into a virtual 3D CAD model for later editing, production and visualization.
The objectives of the WP 2 is the implementation of novel algorithms for surface reconstruction from unstructured point cloud acquired with traditional and innovative 3D scanning systems. Research efforts of the WP2 are divided into two main objectives:
- Fast Reverse Engineering: a tight collaboration among WP1, WP2 and WP3
- Reconstruction of implicit surfaces using methods based on Partial Differential Equation models
Fast Reverse Engineering
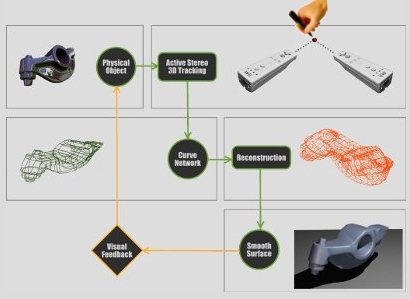
Development of a new method of reverse engineering for fast, simple and interactive acquisition and reconstruction of a virtual 3D model representing an exhisting physical object.
The measurement step is achieved through an active stereovision system made of two infrared cameras (available in the Wii Remote controller) and one infrared light emitter mounted on a pen-like device. The user controls the IR pen, the 3D position of which is tracked by the stereo rig, and can intuitively draw and refine the style lines of the object. The reconstruction of a smooth surface from the curves drawn by the user is obtained through a multi step process that makes uses of subdivision surfaces.
In particular it transforms the mesh associated to the curve network created by the user from a general n-gons mesh to a tri-quad mesh by searching a good solution traversing the tree of all possible subdivisions of an n-sided face into triangles and quads with a greedy strategy and comparing different solution with a score based on the least squares plane. Then the mesh is refined using bilinearly blended Coons patches, producing a so called base mesh and finally a Catmull-Clark subdivision surface scheme is applied to produce a smoother surface.
The remarkable presence of the user during the process and the new way this system proposes to interface with Computer Aided Design software, open up to the investigation of innovative or alternative techniques for Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) such as virtual reality, modal interfaces and different types of feedbacks that should enhance and facilitate the user experience.
paper "A Fast Interactive Reverse-Engineering System "Reconstruction of implicit surfaces using methods based on Partial Differential Equation models
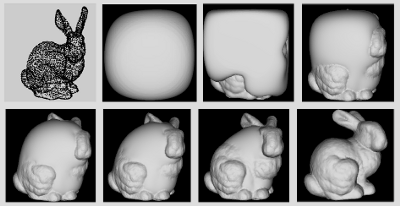
The shape reconstruction problem has several applications in areas that include medical imaging, scientific computing, reverse engineering, virtual simulation, computer graphics, etc. Surface reconstruction consists in finding out the original surface shape from partial information that can include points, pieces of curves, or surfaces. The reconstruction of a 3D virtual model is usually obtained from scattered data points sampled from the surface of the physical 3D object. The acquisition of the data is in general realized through 3D scanning systems which are able to capture a dense sampling usually organized into range images, i.e. sets of distances to the data. The problem is ill-posed, i.e. there is no unique solution. Furthermore the problem can become quite challenging if the topology of the real surface is complicated or even unknown. A good reconstruction algorithm should be able to deal with noisy, non-uniform and incomplete data set in order to construct an arbitrary topology surface with a controlled hole filling strategy, smoothness and a right behavior for deformation, animation and other dynamical operation.
Aim of this project is the 3D reconstruction of virtual model using PDE-based approaches. The implicit surface is obtained by continuously deforming an initial surface following the Partial Differential Equation (PDE)-based diffusion model derived by a minimal volume-like variational formulation. The evolution is driven both by the distance from the data set and by the curvature analytically computed by it. The distance function is computed by implicit local interpolants defined in terms of radial basis functions. Space discretization of the PDE model is obtained by finite co-volume schemes and semi-implicit approach is used in time/scale. The use of a level set method for the numerical computation of the surface reconstruction allows us to handle complex geometry and even changing topology, without the need of user-interactivity. The method proposed is able to produce high quality reconstructions. while solving the hole filling problems and Boolean operations between different data sets.